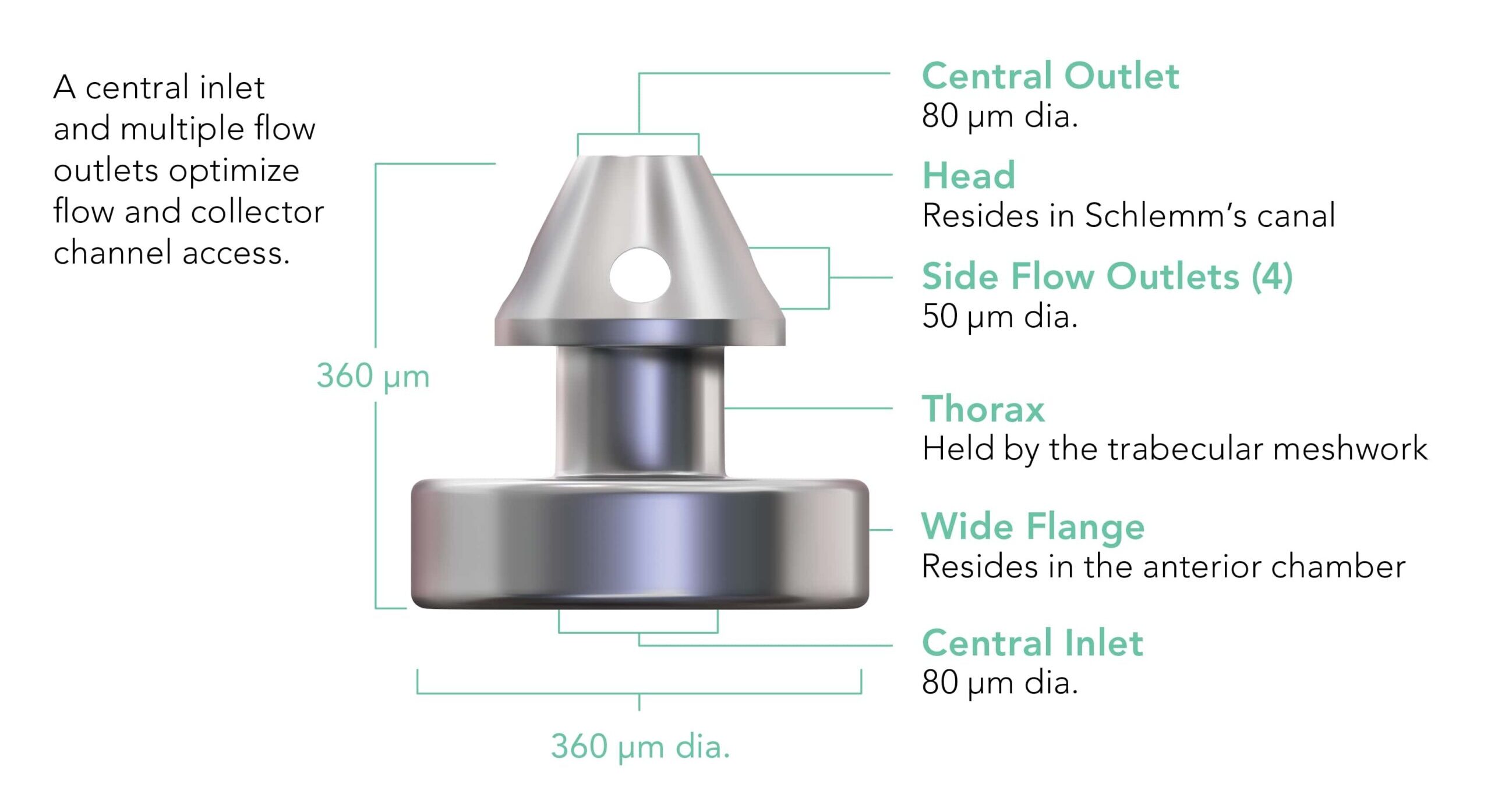
Glaucoma is a disease process that damages the optic nerve of the eye.
The optic nerve is a cable of about a million nerve fibers acting like electrical wires that transmit the visual information received by the eye to the brain for processing. Glaucoma is a disease process that involves loss of these nerve fibers and is the second leading cause of blindness worldwide. It is usually painless, slow, and permanent giving it the moniker the “silent thief of sight.” There are often no symptoms until there is significant, permanent vision loss. Fortunately, through routine dilated eye exams and intra-ocular pressure checks, we can diagnose this condition, and, if treated early, we can prevent blindness.